3x3 Matrix Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Calculator
Calculator Use
3x3 Matrix Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Calculator is a free online tool that displays the Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of a 3x3 Matrix. This online 3x3 Matrix Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Calculator tool performs the calculation faster, and it displays the result in a fraction of seconds.
The procedure to use the 3x3 Matrix Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Calculator is as follows:
Step 1: Enter a values in the input field
Step 2: Now click the "Calculate" button to get the result
Step 3: Finally, The Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of a 3x3 Matrix will be displayed in the output field
What is Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors?
Geometrically, an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction in which it is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed.
Let A be an n×n matrix.
An eigenvector of A is a nonzero vector v in R n such that Av = λv, for some scalar λ.
An eigenvalue of A is a scalar λ such that the equation Av =λv has a nontrivial solution.
If Av = λv for vA = 0, we say that λ is the eigenvalue for v, and that v is an eigenvector for λ.
In Mathematics, an Eigenvalue is a scalar value that is associated with the system of linear equations (also called matrix equations).
The eigenvalue is also known as the latent roots or characteristic root or characteristic value or the proper value. It is associated with the eigenvectors.
The eigenvalues are used in the analysis of linear transformations. The basic equation to represent the eigenvalue is given as AX = λX, Here λ is a scalar value which is the eigenvalue of the matrix A.
What Is Scalar Matrix?
The scalar matrix is a square matrix having a constant value for all the elements of the principal diagonal, and the other elements of the matrix are zero. The scalar matrix is obtained by the product of the identity matrix with a numeric constant value.
The scalar matrix is a square matrix having an equal number of rows and columns.

What Is Identity Matrix?
The identity matrix is a square matrix and is a multiplicative identity for matrices. The identity matrix contains 1 as its diagonal element and all other elements are equal to zero.

What Is Trace of an matrix ?
In linear algebra, the trace of a square matrix A, denoted tr(A),[1] is defined to be the sum of elements on the main diagonal (from the upper left to the lower right) of A. The trace is only defined for a square matrix (n × n).
How to calculate the trace of a matrix?
The trace of a matrix A, designated by tr(A), is the sum of the elements on the main diagonal.

What Is Determinant of a Matrix?
In mathematics, the determinant is a scalar value that is a function of the entries of a square matrix. It allows characterizing some properties of the matrix and the linear map represented by the matrix. In particular, the determinant is nonzero if and only if the matrix is invertible and the linear map represented by the matrix is an isomorphism.
The determinant of a product of matrices is the product of their determinants (the preceding property is a corollary of this one). The determinant of a matrix A is denoted det(A), det A, or |A|.
How to calculate the Determinant of a Matrix?
In the case of a 2 × 2 matrix the determinant can be defined as:

Similarly, for a 3 × 3 matrix A, its determinant is:


|D| = 6×(−2×7 − 5×8) − 1×(4×7 − 5×2) + 1×(4×8 − (−2×2))
= 6×(−54) − 1×(18) + 1×(36)
= −306
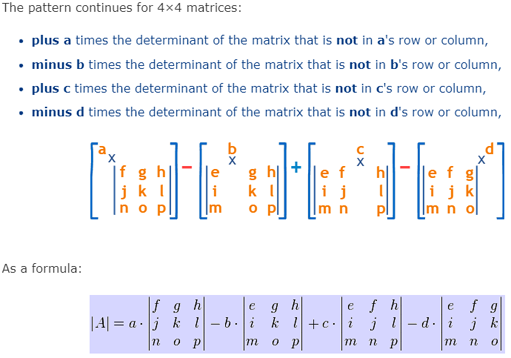
Similarly, for a 4 × 4 matrix A, its determinant is:
What is a Singular Matrix?
We determine whether a matrix is a singular matrix or a non-singular matrix depending on its determinant. The determinant of a matrix 'A' is denoted by 'det A' or '|A|'. If the determinant of a matrix is 0, then it is said to be a singular matrix.
A square matrix that does not have a matrix inverse. A matrix is singular iff its determinant is 0.
How to identify whether the given matrix is a Singular matrix or not ?
A singular matrix is a square matrix if its determinant is 0. i.e., a square matrix A is singular if and only if det A = 0.
Example:

it is a square matrix (of order 3 × 3) and
as det A (or) |A| = 2(0-16)+ 4(28-12)+ 6(16) = 0
What are the properties of a singular matrix?
The determinant of a singular matrix is zero
A non-invertible matrix is referred to as singular matrix, i.e. when the determinant of a matrix is zero, we cannot find its inverse
Singular matrix is defined only for square matrices
There will be no multiplicative inverse for this matrix








